GENOMIC
Mapping
5qF View the map and BAC clones of FISH (data from UCSC genome browser).
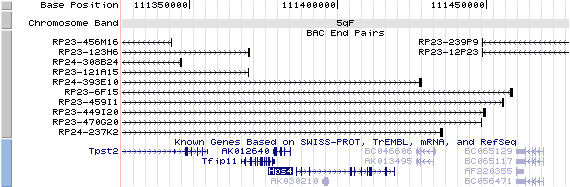
Structure
(assembly 10/03)
Hps4/NM_138646: 13 exons, 33,463 bp, chr5:111,385,848-111,419,310.
The figure shows the structure of le gene. (data from UCSC genome browser).

Regulatory Element
Search the 5'UTR and 1kb upstream regions (seq1=human HPS4, seq2=mouse Hps4) by CONREAL with 80% Position Weight Matrices (PWMs) threshold (view results here).
TRANSCRIPT
RefSeq/ORF
Transcript Reference Sequence (Hps4/NM_138646), 2,545bp, view ORF and the alignment to genomic.
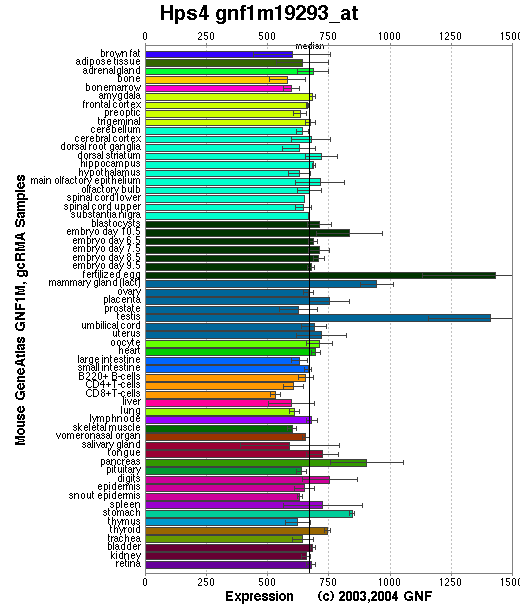
Expression Pattern
Highly expressed in heart, brain, liver and testis. Expressed at lower level in skeletal muscle. 3.6 kb and 3.1 kb transcripts were observed on Northern-blot analysis (Suzuki, et al).
Affymetrix microarray expression pattern in SymAtlas from GNF is shown below.
PROTEIN
Sequence
Le protein (NP_619587 ): 671aa, ExPaSy NiceProt view of Swiss-Prot: Q99KG7.
Synonyms: Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 4 protein homolog; Light-ear protein.
Ortholog
| Species | Human | Chimpanzee | Rat | Chicken | Zebrafish | Drosophila |
| GeneView | HPS4 | 14194 | LOC304555 | 05595 | zgc:56538 | CG4966 |
| Protein | NP_071364 (708aa) | 24438 (708aa) | XP_222245 (545aa) | 08962 (673aa) | NP_956620 (647aa) | Q8MT61 (834aa) |
| Identities | 61%/712aa | 61%/712aa | 77%/550aa | 45%/701aa | 39%/656aa | 26%/328aa |
View multiple sequence alignment (PDF file) by ClustalW and GeneDoc.
Domain
(1) Domains predicted by SMART:
a) low complexity: 171-180
b) low complexity: 467-486
c) low complexity: 514-529
(2) Transmembrane domains predicted by SOSUI: none.
Motif/Site
(1) Predicted results by ScanProsite:
a) N-glycosylation site [pattern] [Warning: pattern with a high probability of occurrence]:
616 - 619 NAST
b) Protein kinase C phosphorylation site [pattern] [Warning: pattern with a high probability of occurrence]:
104 - 106 ScR,
153 - 155 ShR,
210 - 212 TaK,
341 - 343 SsR,
411 - 413 SgR,
472 - 474 SsR,
495 - 497 SgR,
613 - 615 TiR,
639 - 641 TaR.
(2) Predicted results of subprograms by PSORT II:
a) N-terminal signal peptide: none, N-terminal side will be inside.
b) KDEL ER retention motif in the C-terminus: none
c) ER Membrane Retention Signals: none
d) VAC possible vacuolar targeting motif: none
e) Actinin-type actin-binding motif: type 1: none; type 2: none
f) Prenylation motif: none
g) memYQRL transport motif from cell surface to Golgi: none
h) Tyrosines in the tail: none
i) Dileucine motif in the tail: none
3D Model
(1) ModBase: none.
(2) 3D models of protein predicted by SPARKS (fold recognition) below. View the models by PDB2MGIF.
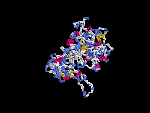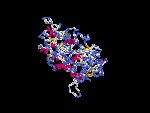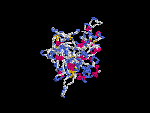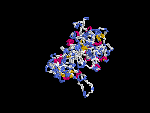
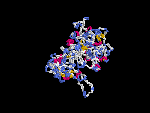
2D-PAGE
This protein does not exist in the current release of SWISS-2DPAGE.
Computed theoretical MW=72,634Da, pI=5.17.
This protein does not exist in the current release of SWISS-2DPAGE.
Computed theoretical MW=72,634Da, pI=5.17.
FUNCTION
Ontology
a) Biological process: melanocyte differentiation, organelle organization and biogenesis.
b) Component of cytoplasmic vesicle.
Location
Cytoplasm, may be associated with membrane fraction.
Interaction
HPS4p is a component of a protein complex termed biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 3 (BLOC-3), where HPS1p is residing as another subunit (Chiang, et al; Martina, et al; Nazarian, et al) (view diagram of BLOC-3 complex here). The BLOC-3 complex is a moderately asymmetric complex with a molecular mass of about 175 kD. The BLOC-3 complex dissociates into smaller complex (BLOC-4) upon Tris treatment and a portion of HPS1 exists in a cytosolic complex (BLOC-5) that does not contain HPS4 (Chiang, et al).
No interactions found in the CuraGen database by searching its drosophila homolog CG4966.
Pathway
Hps4 may be involved in the biogenesis of early melanosomes and the maturation (view diagram of melanosome blockage here) or the structure of cytoplasmic organelles, i.e. melanosomes, platelet dense bodies, lysosomes. Suzuki, et al revealed that Hps4 and Hps1 proteins function in the same pathway of organelle biogenesis. However, the exact mechanism of BLOC-3 in melanosomal biogenesis is lacking. Martina, et al found that Hps1 and Hps4 are components of a cytosolic complex that is involved in the biogenesis of lysosomal-related organelles through a mechanism distinct from that operated by the AP-3 complex (view diagram of BLOC-3 and AP-3 pathway here).
MUTATION
Allele or SNP
1 phenotypic alleles described in MGI:2177742 .
SNPs deposited in dbSNP.
Distribution
| Location | Genomic | cDNA | Protein | Type | Strain | Reference |
| Exon 3 | 148C>T | 148C>T | Q50X | nonsense | le (B6) | Suzuki, et al |
(Numbering of genomic and cDNA sequence is based on the start codon of RefSeq NM_138646.)
Effect
The nonsense Q50X mutation in the Hps4 gene is predicted as nonsense mediated decaying. The Hps1p protein is absent in tissues of le mutant mice (Suzuki, et al).
The nonsense Q50X mutation in the Hps4 gene is predicted as nonsense mediated decaying. The Hps1p protein is absent in tissues of le mutant mice (Suzuki, et al).
PHENOTYPE
Defects in Hps4 are the cause of the light ear (le) mutant. Homozygotes for a spontaneous null mutation exhibit hypopigmentation, prolonged bleeding associated with a platelet defect, reduced secretion of kidney lysosomal enzymes, and resistance to diet-induced atherosclerosis (Novak, et al; Paigen, et al). See more details in the Mouse Locus Catalog#Hps4. The strain is described in more detail in JAX Mice database (B6.-Hps4le/J). le and ep mutants have identical phenotypes. Very few melanosomes of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) are observed in the BLOC-3 mutants Hps1/ep and Hps4/le. A unique feature of ep and le is the presence of very large macromelanosomes within the choroids ( Suzuki, et al). In addition, le/le-ep/ep double-homozygote mice have a phenotype identical to the two homozygous single mutants (Meisler, et al).
REFERENCE
- Chiang PW, Oiso N, Gautam R, Suzuki T, Swank RT, Spritz RA. The Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 1 (HPS1) and HPS4 proteins are components of two complexes, BLOC-3 and BLOC-4, involved in the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 20332-7. PMID: 12663659
- Martina JA, Moriyama K, Bonifacino JS. BLOC-3, a protein complex containing the Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome gene products HPS1 and HPS4. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 29376-84. PMID: 12756248
- Meisler MH, Wanner L, Strahler J. Pigmentation and lysosomal phenotypes in mice doubly homozygous for both light-ear and pale-ear mutant alleles. J Hered 1984; 75: 103-6. PMID: 6232310
- Nazarian R, Falcon-Perez JM, Dell'Angelica EC. Biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 3 (BLOC-3): a complex containing the Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) proteins HPS1 and HPS4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 8770-5. PMID: 12847290
- Novak EK, Hui SW, Swank RT. Platelet storage pool deficiency in mouse pigment mutations associated with seven distinct genetic loci. Blood 1984; 63: 536-44. PMID: 6696991
- Paigen B, Holmes PA, Novak EK, Swank RT. Analysis of atherosclerosis susceptibility in mice with genetic defects in platelet function. Arteriosclerosis 1990; 10: 648-52. PMID: 2369371
- Suzuki T, Li W, Zhang Q, Karim A, Novak EK, Sviderskaya EV, Hill SP, Bennett DC, Levin AV, Nieuwenhuis HK, Fong CT, Castellan C, Miterski B, Swank RT, Spritz RA. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome is caused by mutations in HPS4, the human homolog of the mouse light-ear gene. Nat Genet 2002; 30: 321-4. PMID: 11836498
EDIT HISTORY:
Created by Wei Li: 06/16/2004
Updated by Wei Li: 08/03/2012