GENOMIC
Mapping
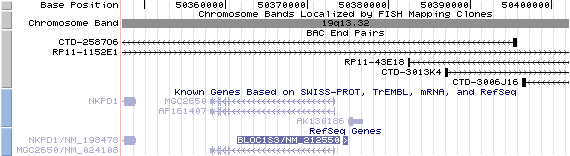
19q13.32. View the map and BAC contig (data from UCSC genome browser).
Structure
(assembly 07/03)
BLOC1S3/NM_212550: 1 exon, 610 bp, chr19:50,374,394-50,375,003.
The figure below shows the structure of the BLOC1S3 gene (data from UCSC genome browser).

Regulatory Element
Search the 5'UTR and 1kb upstream regions (seq1=human BLOC1S3, seq2=mouse rp) by CONREAL with 80% Position Weight Matrices (PWMs) threshold (view results here).
TRANSCRIPT
RefSeq/ORF
HPS8/BLOC1S3 (NM_212550): 609 bp, view ORF and the alignment to genomic.
Expression Pattern
Tissue specificity: Ubiquitously expressed (by similarity).
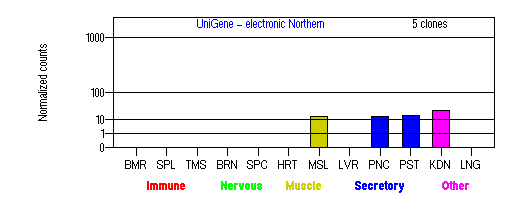
BMR: Bone marrow; SPL: Spleen; TMS: Thymus; BRN: Brain; SPC: Spinal cord; HRT: Heart; MSL: Skeletal muscle; LVR; Liver; PNC: Pancreas; PST: Prostate; KDN: Kidney; LNG: Lung. (data from GeneCards )
PROTEIN
Sequence
BLOC-1 subunit 3
(NP_997715): 202aa.
Synonym: Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 8 protein.
Ortholog
| Species | Mouse | Rat |
| GeneView | rp/Bloc1s3 | LOC308413 |
| Protein | NP_808360 (195aa) | XP_218422 (195aa) |
| Identities | 87%/201aa | 87%/201aa |
View multiple sequence alignment (PDF file) by ClustalW and GeneDoc.
Domain
(1) Domains of predicted by SMART:
low complexity: 6-14, 21-38, 41-55, 59-77, 140-157
(2) Transmembrane domains predicted by SOSUI: none.
Motif/Site
(1) Predicted results by ScanProsite:
a) Alanine-rich region profile : [occurs frequently]
90 - 171: score=9.353
Aeeawgteeapapaparsllqlrlaesqarldhdvaaavsgvyrragrdvaalasrlaaa
qaaglaaahsvrlargdlcalA.
b) Amidation site : [occurs frequently]
4 - 7: qGRR.
c) Casein kinase II phosphorylation site : [occurs frequently]
23 - 26: TetD,
25 - 28: TdsE,
32 - 35: SssE,
33 - 36: SseE,
34 - 37: SeeE,
63 - 66: TdsE,
65 - 68: SepE,
89 - 92: SaeE,
192 - 195: TepE.
d) Protein kinase C phosphorylation site : [occurs frequently]
27 - 29: SeR,
159 - 161: SvR.
e) N-myristoylation site : [occurs frequently]
53 - 58: GLrvAG,
153 - 158: GLaaAH,
188 - 193: GVpgTE.
f) Cell attachment sequence : [occurs frequently]
164 - 166: RGD
g) Tyrosine sulfation site : [occurs frequently]
33 - 47:
sseeeelYlgpsgpt.
(2) Predicted results of subprograms by PSORT II:
a) N-terminal signal peptide: none
b) KDEL ER retention motif in the C-terminus: none
c) ER membrane retention signals: none
d) VAC possible vacuolar targeting motif: none
e) Actinin-type actin-binding motif: type 1: none; type 2: none
f) Prenylation motif: none
g) memYQRL transport motif from cell surface to Golgi: none
h) Tyrosines in the tail: none
i) Dileucine motif in the tail: none
3D Model
(1) ModBase: none.
(2) 3D models predicted by SPARKS (fold recognition) below. View the models by PDB2MGIF.
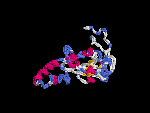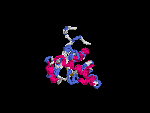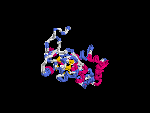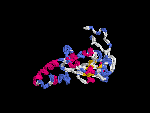
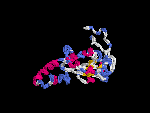
2D-PAGE
This protein does not exist in the current release of SWISS-2DPAGE.
Computed theoretical MW=21,256Da, pI=5.08.
FUNCTION
Ontology
(1) May play a role in intracellular vesicle trafficking.
(2) Protein interaction in BLOC-1.
Location
Cytoplasmic.
Interaction
BLOC-1 subunit 2 is a subunit of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1 (BLOC-1), where it resides with the products of seven other HPS genes, DTNBP1, MU, PLDN, CNO, BLOS1, BLOS2, SNAPAP (Ciciotte, et al; Falcon-Perez , et al; Li, et al; Moriyama, et al; Starcevic, et al). BLOS3 interacts with BLOS2 within the complex ( Starcevic, et al) (view diagram of BLOC-1 complex here). More details about the function of BLOC-1 are described in the HPS7 profile.
Pathway
Involved in the development of lysosome-related organelles, such as melanosomes and platelet-dense granules (view diagram of BLOC-1 pathway here).
MUTATION
Allele or SNP
SNPs deposited in dbSNP.
Distribution
| Location | Genomic | cDNA | Protein | Type | Ethnicity | Reference |
| Exon 1 | 131C>A | 131C>A | S44X | nonsense | Iranian | Cullinane, et al |
| Exon 1 | 448delC | 448delC | Q150delC | frame-shift, 225X | Pakistani | Morgan, et al |
(Numbering of genomic and cDNA sequence is based on the start codon of RefSeq NM_212550.)
Effect
The mutant GFP-tagged protein (224aa) was mislocalized in nucleus compared to a cytoplasmic wild-type protein. No nonsense-mediated decay and destabilization of the BLOC-1 complex was observed to the S44X and Q150delC mutation (Cullinane, et al; Morgan, et al). Aberrant localization of TYRP1, with increased plasma-membrane trafficking, was observed (Cullinane, et al). The residues after Q150 may be important for its normal function (Morgan, et al).
PHENOTYPE
Morgan, et al described a large Pakistani family with six HPS-8 patients. Autozygosity mapping studies have shown these patients were caused by a homozygous frameshift mutation in the BLOC1S3 gene. All patients present cardinal HPS features: hypopigmentation, platelet dysfunction, and visual defects (nystagmus, iris transilluminancy, foveal hypoplasia, reduced visual acuity, and evidence of optic pathway misrouting). Skin biopsy demonstrated abnormal aggregates of melanosomes within basal epidermal keratinocytes. A nonsense mutation in the murine orthologue of BLOC1S3 causes reduced pigmentation (rp) in mouse (Starcevic, et al).
REFERENCE
- Ciciotte SL, Gwynn B, Moriyama K, Huizing M, Gahl WA, Bonifacino JS, Peters LL. Cappuccino, a mouse model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, encodes a novel protein that is part of the pallidin-muted complex (BLOC-1). Blood 2003; 101: 4402-7. PMID: 12576321
- Cullinane AR, Curry JA, Golas G, Pan J, Carmona-Rivera C, Hess RA, White JG, Huizing M, Gahl WA. A BLOC-1 Mutation Screen Reveals a Novel BLOC1S3 Mutation in Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome Type 8 (HPS-8). Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012; 25: 584-91. PMID: 22709368
- Falcon-Perez JM, Starcevic M, Gautam R, Dell'Angelica EC. BLOC-1, a novel complex containing the pallidin and muted proteins involved in the biogenesis of melanosomes and platelet-dense granules. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 28191-9. PMID: 12019270
- Gwynn B, Martina JA, Bonifacino JS, Sviderskaya EV, Lamoreux ML, Bennett DC, Moriyama K, Huizing M, Helip-Wooley A, Gahl WA, Webb LS, Lambert AJ, Peters LL. Reduced pigmentation (rp), a mouse model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, encodes a novel component of the BLOC-1 complex. Blood 2004; 104: 3181-9.PMID: 15265785
- Li W, Zhang Q, Oiso N, Novak EK, Gautam R, O'Brien EP, Tinsley CL, Blake DJ, Spritz RA, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Amato D, Roe BA, Starcevic M, Dell'Angelica EC, Elliott RW, Mishra V, Kingsmore SF, Paylor RE, Swank RT. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 7 (HPS-7) results from mutant dysbindin, a member of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1 (BLOC-1). Nat Genet 2003; 35: 84-9. PMID: 12923531
- Morgan NV, Pasha S, Johnson CA, Ainsworth JR, Eady RA, Dawood B, McKeown C, Trembath RC, Wilde J, Watson SP, Maher ER. A Germline Mutation in BLOC1S3/Reduced Pigmentation Causes a Novel Variant of Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome (HPS8). Am J Hum Genet 2006; 78: 160-6. PMID: 16385460
- Moriyama K, Bonifacino JS. Pallidin is a component of a multi-protein complex involved in the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles. Traffic 2002; 3: 666-77. PMID: 12191018
- Starcevic M, Dell'Angelica EC. Identification of snapin and three novel proteins (BLOS1, BLOS2, and BLOS3/reduced pigmentation) as subunits of biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-1 (BLOC-1). J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 28393-401. PMID: 15102850
EDIT HISTORY:
Created by Wei Li, 07/08/2004
Updated by Wei Li, 01/20/2006
Updated by Wei Li, 08/03/2012
Updated by Wei Li, 06/13/2013