GENOMIC
Mapping
16qA1. View the map and BAC clones (data from UCSC genome browser).
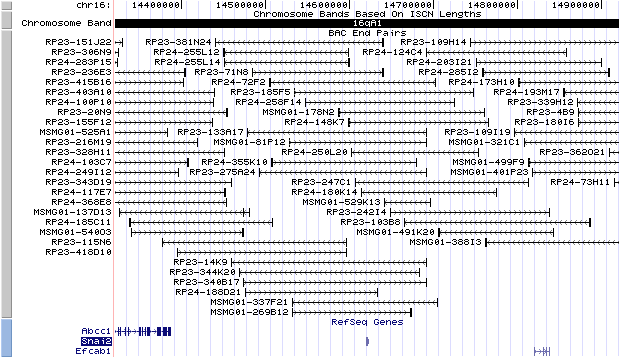
Structure
(assembly 02/2006)
Snai2/NM_011415: 3 exons, 3,522 bp, chr16:14619437-14622958.
The figure below shows the structure of the Snai2 gene (data from UCSC genome browser).

Regulatory Element
Search the 5'UTR and 1kb upstream regions (seq1=mouse Snai2, seq2=human SNAI2) by CONREAL with 80% Position Weight Matrices (PWMs) threshold (view results here).
TRANSCRIPT
RefSeq/ORF
Snai2 ( NM_011415), 2,084 bp, view ORF and the alignment to genomic.
Expression Pattern
Slugh expression is first detected in extraembryonic mesoderm and is later detected in many mesodermal subsets, although it is not detected in the primitive streak (Jiang et al.).
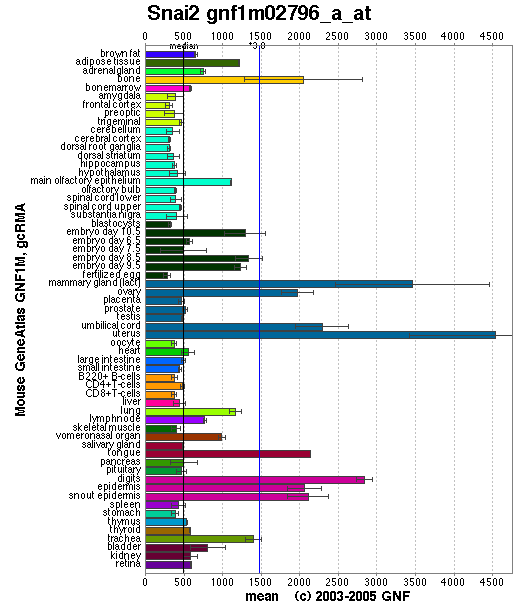
Affymetrix microarray expression pattern in SymAtlas from GNF is shown below.
Browse more information in Entrez Gene, UCSC Gene Sorter, MGI.
PROTEIN
Sequence
snail homolog 2 (NP_035545): 269 aa, UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entry P97469.
Ortholog
Species Human
Chimpanzee Dog Fowl GeneView
SNAI2
SNAI2
LOC486940
LOC421112
Protein
NP_003059 (268 aa)
XP_519753.2 (268 aa)
XP_544069.1 (268 aa)
XP_419196.1 (268 aa)
Identities
242/269 (89%) 242/269 (89%) 243/269 (90%) 236/269 (87%)
View multiple sequence alignment (PDF file) by ClustalW and GeneDoc. View evolutionary tree by TreeView.
Domain
(1) Domains predicted by SMART:
a) low complexity: 60-84
b) low complexity: 88-105
c) ZnF_C2H2: 129-151
d) ZnF_C2H2: 160-182
e) ZnF_C2H2: 186-208
f) ZnF_C2H2: 214-236
g) ZnF_C2H2: 242-269
(2) Transmembrane domains predicted by SOSUI:
This amino acid sequence is of a SOLUBLE PROTEIN.
(3) Graphic view of InterPro domain structure.
Motif/Site
(1) Predicted results by ScanProsite:
a) N-glycosylation site:
Site : 12 to 15 NASK.
Site : 18 to 21 NYSE.
Site : 135 to 138 NKTY.
Site : 246 to 249 NCSK.
b) Protein kinase C phosphorylation site:
Site : 14 to 16 SKK.
Site : 96 to 98 SSK.
Site : 156 to 158 SRK.
Site : 161 to 163 SCK.
c) Casein kinase II phosphorylation site:
Site : 20 to 23 SELD.
Site : 96 to 99 SSKD.
Site : 101 to 104 SGSE.
Site : 108 to 111 SDEE.
Site : 235 to 238 THSD.
d) Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site:
Site : 163 to 169 KYCDKEY.
e) N-myristoylation site:
Site : 264 to 269 GCCVAH.
f) Zinc finger C2H2 type domain signature.
Site : 131 to 151 CNLCNKTYSTFSGLAKHKQLH.
Site : 162 to 182 CKYCDKEYVSLGALKMHIRTH.
Site : 188 to 208 CKICGKAFSRPWLLQGHIRTH.
Site : 216 to 236 CPHCNRAFADRSNLRAHLQTH.
Site : 186 to 208 CVCKICGKAFSRPWLLQGHIRTH.
(2) Predicted results of subprograms by PSORT II:
a) N-terminal signal peptide: none
b) Tentative number of TMS(s) for the threshold 0.5: 0
c) KDEL ER retention motif in C-terminus: none
d) ER membrane retention signals: none
e) VAC possible vacuolar targeting motif: none
f) Actinin-type actin-binding motif: type 1: none; type 2: none
g) Prenylation motif: none
h) memYQRL transport motif from cell surface to Golgi: none
i) Tyrosines in the tail: none
j) Dileucine motif in the tail: none
3D Model
(1) ModBase predicted 3D structure of P97469 from UCSC Genome Sorter:
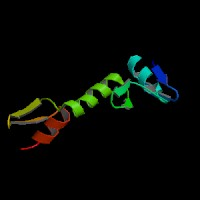
From left to right: Front, Top, and Side views of predicted protein.
2D-PAGE
This protein does not exist in the current release of SWISS-2DPAGE.
Computed theoretical MW=30,003.2Da, pI=9.07 (NP_035545).
| Species | Human | Chimpanzee | Dog | Fowl |
| GeneView | SNAI2 | SNAI2 | LOC486940 | LOC421112 |
| Protein | NP_003059 (268 aa) | XP_519753.2 (268 aa) | XP_544069.1 (268 aa) | XP_419196.1 (268 aa) |
| Identities | 242/269 (89%) | 242/269 (89%) | 243/269 (90%) | 236/269 (87%) |
View multiple sequence alignment (PDF file) by ClustalW and GeneDoc. View evolutionary tree by TreeView.
Domain
(1) Domains predicted by SMART:
a) low complexity: 60-84
b) low complexity: 88-105
c) ZnF_C2H2: 129-151
d) ZnF_C2H2: 160-182
e) ZnF_C2H2: 186-208
f) ZnF_C2H2: 214-236
g) ZnF_C2H2: 242-269
(2) Transmembrane domains predicted by SOSUI:
This amino acid sequence is of a SOLUBLE PROTEIN.
(3) Graphic view of InterPro domain structure.
Motif/Site
(1) Predicted results by ScanProsite:
a) N-glycosylation site:
Site : 12 to 15 NASK.
Site : 18 to 21 NYSE.
Site : 135 to 138 NKTY.
Site : 246 to 249 NCSK.
b) Protein kinase C phosphorylation site:
Site : 14 to 16 SKK.
Site : 96 to 98 SSK.
Site : 156 to 158 SRK.
Site : 161 to 163 SCK.
c) Casein kinase II phosphorylation site:
Site : 20 to 23 SELD.
Site : 96 to 99 SSKD.
Site : 101 to 104 SGSE.
Site : 108 to 111 SDEE.
Site : 235 to 238 THSD.
d) Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site:
Site : 163 to 169 KYCDKEY.
e) N-myristoylation site:
Site : 264 to 269 GCCVAH.
f) Zinc finger C2H2 type domain signature.
Site : 131 to 151 CNLCNKTYSTFSGLAKHKQLH.
Site : 162 to 182 CKYCDKEYVSLGALKMHIRTH.
Site : 188 to 208 CKICGKAFSRPWLLQGHIRTH.
Site : 216 to 236 CPHCNRAFADRSNLRAHLQTH.
Site : 186 to 208 CVCKICGKAFSRPWLLQGHIRTH.
(2) Predicted results of subprograms by PSORT II:
a) N-terminal signal peptide: none
b) Tentative number of TMS(s) for the threshold 0.5: 0
c) KDEL ER retention motif in C-terminus: none
d) ER membrane retention signals: none
e) VAC possible vacuolar targeting motif: none
f) Actinin-type actin-binding motif: type 1: none; type 2: none
g) Prenylation motif: none
h) memYQRL transport motif from cell surface to Golgi: none
i) Tyrosines in the tail: none
j) Dileucine motif in the tail: none
3D Model
(1) ModBase predicted 3D structure of P97469 from UCSC Genome Sorter:



From left to right: Front, Top, and Side views of predicted protein.
2D-PAGE
This protein does not exist in the current release of SWISS-2DPAGE.
Computed theoretical MW=30,003.2Da, pI=9.07 (NP_035545).
FUNCTION
Ontology
(1) Biological process: DNA binding, DNA-dependent regulation of transcription, sensory perception of sound.
(2) Transcriptional repressor.
(3) Zinc ion binding.
(4) Involved in the generation and migration of neural crest cells. Ectoderm and mesoderm interaction.
Location
Nucleus.
Interaction
This gene encodes a member of the Snail family of C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factors. The encoded protein acts as a transcriptional repressor that binds to E-box motifs and is also likely to repress E-cadherin transcription in breast carcinoma. This protein is involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transitions and has antiapoptotic activity.
View co-occured partners in literature searched by PPI Finder.
Pathway
Slug was first cloned as a Snail family member in chickens and has been implicated in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Adhesion Pathway in KEGG.
MUTATION
Allele or SNP
3 phenotypic alleles of Snai2 are described in MGI:1096393.
SNPs deposited in dbSNP Build 128.
Distribution
The 3 phenotypic alleles inclede 2 knock-outs and 1 other targeted.
(Numbering of cDNA sequence is based on the start codon of RefSeq NM_011415. view ORF here.)
Effect
Mutations in this gene result in growth retardation and eyelid deformities.
PHENOTYPE
The initial description of Snai2 knockout mice reported no neural crest defects and described normal melanocyte generation, migration, and development (Jiang et al.). But it is required for full pigmentation of the coat. Slug(-/-) mice have diluted coat color, a white forehead blaze, and areas of depigmentation on the ventral body, tail and feet, mimicking the phenotype of Waardenburg syndrome (Sanchez-Martin et al.). Hyperactivity and circling behaviors observed in some Slug(-/-) mice suggest a vestibulo-cochlear disorder. In addition, Snai2(-/-) mice exhibit cleft palate(Murray et al.).
REFERENCE
- Jiang R, Lan Y, Norton CR, Sundberg JP, Gridley T. The Slug gene is not essential for mesoderm or neural crest development in mice. Dev Biol 1998; 198:277-285. PMID: 9659933
- Murray SA, Oram KF, Gridley T. Multiple functions of Snail family genes during palate development in mice. Development 2007; 134:1789-97. PMID: 17376812
- Sanchez-Martin M, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Perez-Losada J, Sagrera A, Read AP, Sanchez-Garcia I. SLUG (SNAI2) deletions in patients with Waardenburg disease. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11:3231-3236.PMID: 12444107