GENOMIC
Mapping
4q12. View the map and BAC clones (data from UCSC genome browser).
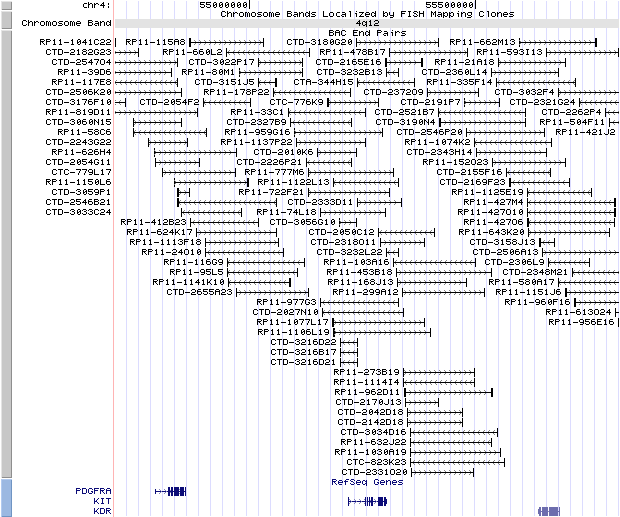
Structure
(assembly 03/2006)
KIT (BC071593): 21 exons, 82,774 bp, chr4:55218863-55301636.
Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
The figure below shows the structure of the KIT gene (data from UCSC genome browser).

Regulatory Element
Search the 5'UTR and 1kb upstream regions (seq1=mouse Kit, seq2=human KIT) by CONREAL with 80% Position Weight Matrices (PWMs) threshold (view results here).
TRANSCRIPT
RefSeq/ORF
KIT (NM_000222), 5,084 bp, view ORF and the alignment to genomic.
Note: Variant (NM_001093772) uses an alternate in-frame splice site in the central coding region, compared to NM_000222 (encoding isoform 1), resulting in a shorter protein (isoform 2).
Expression Pattern
Affymetrix microarray expression pattern in SymAtlas from GNF is shown below.
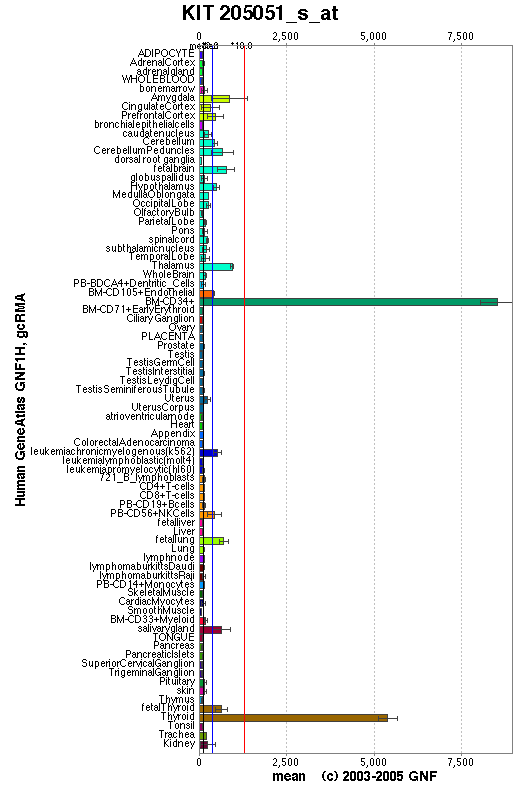
View more information in Entrez Gene, or UCSC Gene Sorter, or GeneCards.
PROTEIN
Sequence
v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog
(NP_000213): 976 aa, UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entry P10721.
Ortholog
Species
Chimpanzee Dog Mouse Rat Chicken GeneView
KIT
KIT
Kit
Kit
KIT
Protein
XP_517285 (1,073 aa)
NP_001003181 (975 aa)
NP_066922(975 aa)
NP_071600 (978 aa)
NP_989692 (960 aa)
Identities
969/976 (99%) 861/979 (87%) 803/979 (82%) 820/978 (83%) 628/941 (66%)
View multiple sequence alignment (PDF file) by ClustalW and GeneDoc. View evolutionary tree by TreeView.
Domain
(1) Domains predicted by SMART:
a) signal peptide: 1-25
b) IG_like: 43-112
c) low complexity: 206-220
d) IGc2: 224-297
e) IG_like: 320-410
f) transmembrane: 521-543
g) TyrKc: 589-924
(2) Transmembrane domains predicted by SOSUI:
This amino acid sequence is of a MEMBRANE PROTEIN
which have 2 transmembrane helices.
No. N terminal transmembrane region C terminal type length 1 3 GARGAWDFLCVLLLLLRVQTGS 24 SECONDARY 22 2 522 FTPLLIGFVIVAGMMCIIVMILT 544 PRIMARY 23
(3) Graphic view of InterPro domain structure.
Motif/Site
(1) Predicted results by ScanProsite:
a)N-glycosylation site:
Site : 130 to 133 NDTL.
Site : 145 to 148 NYSL.
Site : 283 to 286 NDSG.
Site : 293 to 296 NNTF.
Site : 300 to 303 NVTT.
Site : 320 to 323 NTTV.
Site : 352 to 355 NRTF.
Site : 367 to 370 NESN.
Site : 463 to 466 NSSG.
Site : 486 to 489 NGTV.
Site : 819 to 822 NDSN.
b) cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation site:
Site : 685 to 688 KRDS.
Site : 738 to 741 KRRS.
Site : 913 to 916 KRPT.
c) Protein kinase C phosphorylation site:
Site : 84 to 86 TEK.
Site : 92 to 94 TGK.
Site : 98 to 100 TNK.
Site : 147 to 149 SLK.
Site : 174 to 176 SVK.
Site : 197 to 199 SEK.
Site : 234 to 236 TIK.
Site : 245 to 247 TWK.
Site : 279 to 281 SAR.
Site : 356 to 358 TDK.
Site : 544 to 546 TYK.
Site : 632 to 634 TER.
Site : 741 to 743 SVR.
Site : 916 to 918 TFK.
Site : 954 to 956 SVR.
d) Casein kinase II phosphorylation site:
Site : 30 to 33 SPGE.
Site : 139 to 142 TDPE.
Site : 234 to 237 TIKD.
Site : 303 to 306 TTLE.
Site : 354 to 357 TFTD.
Site : 365 to 368 SENE.
Site : 395 to 398 SNSD.
Site : 411 to 414 TKPE.
Site : 476 to 479 SSID.
Site : 632 to 635 TERE.
Site : 692 to 695 SKQE.
Site : 713 to 716 SCSD.
Site : 717 to 720 STNE.
Site : 734 to 737 TKAD.
Site : 746 to 749 SYIE.
Site : 905 to 908 TCWD.
e) Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site:
Site : 383 to 390 KGTEGGTY.
Site : 602 to 609 KVVEATAY.
f) N-myristoylation site:
Site : 3 to 8 GARGAW.
Site : 102 to 107 GLSNSI.
Site : 286 to 291 GVFMCY.
Site : 384 to 389 GTEGGT.
Site : 387 to 392 GGTYTF.
Site : 424 to 429 GMLQCV.
Site : 487 to 492 GTVECK.
Site : 610 to 615 GLIKSD.
Site : 648 to 653 GNHMNI.
Site : 961 to 966 GSTASS.
g) ATP/GTP-binding site motif A (P-loop):
Site : 493 to 500 AYNDVGKT.
h) Protein kinases ATP-binding region signature:
Site : 595 to 623 LGAGAFGKVVEATAYGLIKSDAAMTVAVK.
i) Tyrosine protein kinases specific active-site signature:
Site : 788 to 800 CIHRDLAARNILL.
j) Receptor tyrosine kinase class III signature:
Site : 648 to 661 GNHMNIVNLLGACT.
(2) Predicted results of subprograms by PSORT II:
a) Seems to have a cleavable signal peptide (1 to 22)
b) Tentative number of TMS(s) for the threshold 0.5: 2
Number of TMS(s) for threshold 0.5: 1
INTEGRAL Likelihood =-12.74 Transmembrane 526 - 542
PERIPHERAL Likelihood = 2.49 (at 200)
ALOM score: -12.74 (number of TMSs: 1)
c) KDEL ER retention motif in C-terminus: none
d) ER membrane retention signals: XXRR-like motif in the N-terminus: RGAR
e) VAC possible vacuolar targeting motif: none
f) Actinin-type actin-binding motif: type 1: none; type 2: none
g) Prenylation motif: none
h) memYQRL transport motif from cell surface to Golgi: none
i) Tyrosines in the tail: too long tail
j) Dileucine motif in the tail: found
LL at 656
LL at 678
LL at 706
LL at 769
LL at 799
LL at 970
3D Model
ModBase predicted 3D structure of P10721 from UCSC Genome Sorter:
From left to right: Front, Top, and Side views of predicted protein.
Protein Data Bank (PDB) 3-D Structure of P10721
2D-PAGE
This protein does not exist in the current release of SWISS-2DPAGE.
Computed theoretical MW=109,864.5Da, pI=6.54.
| Species | Chimpanzee | Dog | Mouse | Rat | Chicken |
| GeneView | KIT | KIT | Kit | Kit | KIT |
| Protein | XP_517285 (1,073 aa) | NP_001003181 (975 aa) | NP_066922(975 aa) | NP_071600 (978 aa) | NP_989692 (960 aa) |
| Identities | 969/976 (99%) | 861/979 (87%) | 803/979 (82%) | 820/978 (83%) | 628/941 (66%) |
View multiple sequence alignment (PDF file) by ClustalW and GeneDoc. View evolutionary tree by TreeView.
Domain
(1) Domains predicted by SMART:
a) signal peptide: 1-25
b) IG_like: 43-112
c) low complexity: 206-220
d) IGc2: 224-297
e) IG_like: 320-410
f) transmembrane: 521-543
g) TyrKc: 589-924
(2) Transmembrane domains predicted by SOSUI:
This amino acid sequence is of a MEMBRANE PROTEIN
which have 2 transmembrane helices.
| No. | N terminal | transmembrane region | C terminal | type | length |
| 1 | 3 | GARGAWDFLCVLLLLLRVQTGS | 24 | SECONDARY | 22 |
| 2 | 522 | FTPLLIGFVIVAGMMCIIVMILT | 544 | PRIMARY | 23 |
(3) Graphic view of InterPro domain structure.
Motif/Site
(1) Predicted results by ScanProsite:
a)N-glycosylation site:
Site : 130 to 133 NDTL.
Site : 145 to 148 NYSL.
Site : 283 to 286 NDSG.
Site : 293 to 296 NNTF.
Site : 300 to 303 NVTT.
Site : 320 to 323 NTTV.
Site : 352 to 355 NRTF.
Site : 367 to 370 NESN.
Site : 463 to 466 NSSG.
Site : 486 to 489 NGTV.
Site : 819 to 822 NDSN.
b) cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation site:
Site : 685 to 688 KRDS.
Site : 738 to 741 KRRS.
Site : 913 to 916 KRPT.
c) Protein kinase C phosphorylation site:
Site : 84 to 86 TEK.
Site : 92 to 94 TGK.
Site : 98 to 100 TNK.
Site : 147 to 149 SLK.
Site : 174 to 176 SVK.
Site : 197 to 199 SEK.
Site : 234 to 236 TIK.
Site : 245 to 247 TWK.
Site : 279 to 281 SAR.
Site : 356 to 358 TDK.
Site : 544 to 546 TYK.
Site : 632 to 634 TER.
Site : 741 to 743 SVR.
Site : 916 to 918 TFK.
Site : 954 to 956 SVR.
d) Casein kinase II phosphorylation site:
Site : 30 to 33 SPGE.
Site : 139 to 142 TDPE.
Site : 234 to 237 TIKD.
Site : 303 to 306 TTLE.
Site : 354 to 357 TFTD.
Site : 365 to 368 SENE.
Site : 395 to 398 SNSD.
Site : 411 to 414 TKPE.
Site : 476 to 479 SSID.
Site : 632 to 635 TERE.
Site : 692 to 695 SKQE.
Site : 713 to 716 SCSD.
Site : 717 to 720 STNE.
Site : 734 to 737 TKAD.
Site : 746 to 749 SYIE.
Site : 905 to 908 TCWD.
e) Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site:
Site : 383 to 390 KGTEGGTY.
Site : 602 to 609 KVVEATAY.
f) N-myristoylation site:
Site : 3 to 8 GARGAW.
Site : 102 to 107 GLSNSI.
Site : 286 to 291 GVFMCY.
Site : 384 to 389 GTEGGT.
Site : 387 to 392 GGTYTF.
Site : 424 to 429 GMLQCV.
Site : 487 to 492 GTVECK.
Site : 610 to 615 GLIKSD.
Site : 648 to 653 GNHMNI.
Site : 961 to 966 GSTASS.
g) ATP/GTP-binding site motif A (P-loop):
Site : 493 to 500 AYNDVGKT.
h) Protein kinases ATP-binding region signature:
Site : 595 to 623 LGAGAFGKVVEATAYGLIKSDAAMTVAVK.
i) Tyrosine protein kinases specific active-site signature:
Site : 788 to 800 CIHRDLAARNILL.
j) Receptor tyrosine kinase class III signature:
Site : 648 to 661 GNHMNIVNLLGACT.
(2) Predicted results of subprograms by PSORT II:
a) Seems to have a cleavable signal peptide (1 to 22)
b) Tentative number of TMS(s) for the threshold 0.5: 2
Number of TMS(s) for threshold 0.5: 1
INTEGRAL Likelihood =-12.74 Transmembrane 526 - 542
PERIPHERAL Likelihood = 2.49 (at 200)
ALOM score: -12.74 (number of TMSs: 1)
c) KDEL ER retention motif in C-terminus: none
d) ER membrane retention signals: XXRR-like motif in the N-terminus: RGAR
e) VAC possible vacuolar targeting motif: none
f) Actinin-type actin-binding motif: type 1: none; type 2: none
g) Prenylation motif: none
h) memYQRL transport motif from cell surface to Golgi: none
i) Tyrosines in the tail: too long tail
j) Dileucine motif in the tail: found
LL at 656
LL at 678
LL at 706
LL at 769
LL at 799
LL at 970
3D Model
ModBase predicted 3D structure of P10721 from UCSC Genome Sorter:



Protein Data Bank (PDB) 3-D Structure of P10721



2D-PAGE
This protein does not exist in the current release of SWISS-2DPAGE.
Computed theoretical MW=109,864.5Da, pI=6.54.
FUNCTION
Ontology
(1) Biological process: hemopoiesis, epithelial cell proliferation, neural crest cell migration, signal transduction, spermatogenesis, protein kinase cascade.
(2) Cytokine-mediated signaling pathway.
(3) Receptor activity.
(4) Receptor signaling protein tyrosine kinase activity, ATP binding.
(5) Regulation of pigmentation during development.
Location
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus.
Interaction
C-kit was first identified as the cellular homolog of the feline sarcoma viral oncogene v-kit. This protein is a type 3 transmembrane receptor for MGF (mast cell growth factor, also known as stem cell factor). It has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. Binding of the ligands leads to the autophosphorylation of KIT and its association with substrates such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (Pi3K).
View interactions in HPRD
View co-occured partners in literature searched by PPI Finder.
Pathway
Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor precursor (EC 2.7.10.1) (SCFR) (Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Kit) (c-kit) (CD117 antigen).
Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction , Melanogenesis, Hematopoietic cell lineage in KEGG.
MUTATION
Allele or SNP
57 mutations deposited in HGMD.
SNPs deposited in dbSNP.
Selected allelic examples described in OMIM.
Distribution
Except the mutations deposited in HGMD, other novel mutations of KIT are liste here.
(1) In Chinese piebaldism patients, novel missense mutations were reported: c.2528G>A (p.S850N) (Deng, et al (2005)), c.1784T>C (p.L595P) (Lin, et al (2006)).
Note that the numbering of the mutations in HGMD is based on KIT cDNA (NM_000222), view ORF here.
Effect
PHENOTYPE
Defects in KIT are a cause of piebaldism [MIM:172800]. Piebaldism is an autosomal dominant genetic developmental abnormality of pigmentation characterized by congenital patches of white skin (leucoderma) and hair (poliosis) that lack melanocytes. Its typical manifestations include a triangular white forelock and hyperpigmented macules on depigmented patches and normal skin. Depigmented patches are mainly found on the scalp, forehead, trunk and limbs, and melanocytes are completely absent in the lesions. Piebaldism has been thought to be a disease due to defective proliferation or migration of melanoblasts from the neural crest during early embryonic development.
Defects in KIT are a cause of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) [MIM:606764].
Defects in KIT have been associated with testicular tumors [MIM:273300]. It includes germ cell tumor (GCT) or testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT).
REFERENCE
- Deng WP, Huang YS, Lu C, Lan W, Zhu GX, Lin QD, Feng PY. [A novel KIT gene mutation from a family with piebaldism in the southern part of China]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2005; 22:668-70. Chinese. PMID: 16331568
- Lin ZM, Xu Z, Bu DF, Yang Y.New mutations of KIT gene in two Chinese patients with piebaldism. Br J Dermatol 2006; 155:1303-4. No abstract available. PMID: 17107413